When do teeth problems start in pregnancy?
Dental problems during pregnancy can occur at any time, but they are most likely to start or worsen during the second trimester. However, it’s important to note that not all pregnant individuals will experience dental issues, and the severity can vary.
Here’s a general timeline of dental problems during pregnancy:
- First Trimester: During the first trimester, many women experience morning sickness, which can lead to increased acid exposure in the mouth due to vomiting. This acid can contribute to tooth erosion and enamel damage. Pregnant individuals may also experience changes in taste and smell, which can affect their oral hygiene habits and dietary choices.
- Second Trimester: The second trimester is often considered the “honeymoon phase” of pregnancy. Many women feel better during this time, and dental issues may temporarily improve. However, hormonal changes can still affect oral health, increasing the risk of gum problems like gingivitis.
- Third Trimester: As pregnancy progresses into the third trimester, some dental issues may worsen. Hormonal changes and increased blood flow can make the gums more susceptible to inflammation and bleeding. This stage may also bring physical discomfort, making dental care and maintenance more challenging.
Common dental problems during pregnancy include:
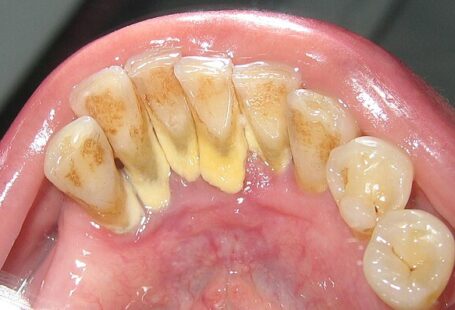
- Gingivitis: Hormonal changes can lead to an increased risk of gum inflammation and gingivitis. Gingivitis can cause redness, swelling, and bleeding of the gums.
- Pregnancy Tumors: Some pregnant individuals develop pregnancy tumors, which are non-cancerous growths on the gums. These usually occur in response to irritation or inflammation and can be related to hormonal changes.
- Tooth Decay: Changes in dietary habits, cravings for sugary foods, and morning sickness can contribute to an increased risk of tooth decay and enamel erosion.
To promote good oral health during pregnancy and minimize dental problems, consider the following tips:
- Regular Dental Checkups: Continue to visit your dentist for regular checkups and cleanings, informing them of your pregnancy. It’s safe to have dental treatments like cleanings and fillings during pregnancy.
- Oral Hygiene: Maintain good oral hygiene by brushing your teeth twice a day with fluoride toothpaste and flossing daily.
- Rinse After Vomiting: If you experience morning sickness, rinse your mouth with water or a fluoride mouthwash after vomiting to help neutralize acids.
- Balanced Diet: Eat a balanced diet that’s rich in nutrients, including calcium and vitamin D, which are essential for healthy teeth and bones.
- Stay Hydrated: Drink plenty of water to help combat dry mouth and promote saliva production.
- Limit Sugar Intake: Reduce your consumption of sugary foods and beverages to minimize the risk of tooth decay.
- Chew Sugar-Free Gum: Chewing sugar-free gum can help stimulate saliva production and reduce the risk of tooth decay.
If you experience dental problems during pregnancy, consult your dentist promptly to address any issues and receive appropriate treatment. Maintaining good oral health during pregnancy is essential for your well-being and the health of your baby.
Are teeth problems common in pregnancy?
Dental problems, such as gum issues and tooth decay, are relatively common during pregnancy. This is often attributed to hormonal changes, changes in dietary habits, and other factors associated with pregnancy. However, the severity and extent of dental problems can vary among individuals. Common dental issues during pregnancy include:
- Gingivitis: Hormonal changes during pregnancy can lead to an increased risk of gum inflammation and gingivitis. Symptoms may include redness, swelling, and bleeding of the gums. Gingivitis is one of the most prevalent dental issues during pregnancy.
- Pregnancy Tumors: Some pregnant individuals develop small, non-cancerous growths on the gums known as pregnancy tumors. These growths typically occur in response to irritation or inflammation and are more common during the second trimester.
- Tooth Decay: Changes in dietary habits, cravings for sugary foods, and morning sickness (which can expose teeth to stomach acid) can contribute to an increased risk of tooth decay and enamel erosion during pregnancy.
- Dry Mouth: Some pregnant women may experience dry mouth, which can increase the risk of tooth decay as saliva plays a vital role in protecting teeth from acid and bacteria.
- Enamel Erosion: Morning sickness and acid reflux during pregnancy can result in acid exposure to the teeth, potentially leading to enamel erosion.
- Increased Blood Flow: Pregnancy can lead to increased blood flow to the gums, making them more susceptible to inflammation, bleeding, and gum problems.
It’s important to note that while these dental issues are common during pregnancy, they are not inevitable. Many pregnant individuals maintain excellent oral health throughout their pregnancies by practicing good oral hygiene and seeking regular dental care.
To promote good oral health during pregnancy and minimize dental problems:
- Continue to visit your dentist for regular checkups and cleanings, and inform them of your pregnancy.
- Maintain good oral hygiene practices by brushing your teeth twice a day with fluoride toothpaste and flossing daily.
- Rinse your mouth with water or a fluoride mouthwash after vomiting if you experience morning sickness.
- Eat a balanced diet rich in nutrients, including calcium and vitamin D, which are essential for healthy teeth and bones.
- Stay hydrated by drinking plenty of water to help combat dry mouth and promote saliva production.
- Limit your consumption of sugary foods and beverages to reduce the risk of tooth decay.
If you experience dental problems during pregnancy, consult your dentist promptly to address any issues and receive appropriate treatment. It’s important to prioritize oral health during pregnancy for your well-being and the health of your baby.
Which trimester is safe for dental treatment?
Dental treatment is generally considered safe during all trimesters of pregnancy, but there are some considerations to keep in mind to ensure the safety and comfort of both the pregnant individual and the developing baby. Dental care is essential during pregnancy, as maintaining good oral health contributes to overall well-being.
Here are some guidelines for dental treatment during each trimester:
- First Trimester (Weeks 1-12): Most routine dental procedures, including cleanings and preventive care, can be safely performed during the first trimester. However, some pregnant individuals may experience morning sickness and increased gag reflex during this time, so it’s a good idea to inform your dentist about any pregnancy-related discomforts. Elective dental procedures and X-rays are typically postponed until after the first trimester if possible, to minimize potential risks during fetal development.
- Second Trimester (Weeks 13-27): The second trimester is often considered the safest time for dental treatment. By this time, the baby’s major organ systems have formed, and the risk of complications from dental procedures is lower. Most dental treatments, including X-rays deemed necessary for diagnostic purposes, can be performed during the second trimester with minimal risk.
- Third Trimester (Weeks 28-40+): Dental treatment is still safe during the third trimester, but some pregnant individuals may experience physical discomfort due to the size and position of the baby. It’s advisable to schedule dental appointments earlier in the trimester if possible. Dental procedures that require long periods of lying on your back may be more challenging at this stage, so inform your dentist if you are experiencing discomfort.
Additional considerations for dental treatment during pregnancy include:
- Medications: Inform your dentist and healthcare provider about your pregnancy and any medications you are taking, including prenatal vitamins and supplements. Your dentist will consider this information when planning your dental treatment.
- Local Anesthetics: Local anesthetics used in dental procedures are generally safe during pregnancy. Your dentist will use the lowest effective dose.
- Radiographs (X-rays): If X-rays are necessary, your dentist will take precautions to minimize radiation exposure. A leaded apron and thyroid collar can be used to protect you and the baby.
- Elective Procedures: Elective procedures like teeth whitening and cosmetic treatments are typically postponed until after pregnancy to minimize potential risks.
Overall, maintaining good oral health during pregnancy is essential. If you have dental concerns or issues, it’s best to consult with your dentist, who can provide appropriate guidance and treatment tailored to your specific needs while considering your pregnancy.
Does pregnancy make teeth weak?
Pregnancy itself does not make teeth weaker, but it can contribute to changes in oral health and may indirectly affect the condition of your teeth. Some of the factors related to pregnancy that can impact oral health include:
- Hormonal Changes: Pregnancy leads to hormonal fluctuations, particularly an increase in estrogen and progesterone. These hormonal changes can affect the oral tissues, making the gums more sensitive and susceptible to inflammation. This heightened sensitivity can contribute to an increased risk of gum problems, such as gingivitis and pregnancy tumors.
- Morning Sickness: Many pregnant individuals experience morning sickness, which involves vomiting. Frequent vomiting can expose teeth to stomach acid, which can lead to enamel erosion and tooth decay over time.
- Cravings and Dietary Changes: Pregnancy cravings can sometimes lead to an increased consumption of sugary foods and beverages. Higher sugar intake can contribute to a higher risk of tooth decay.
- Dry Mouth: Some pregnant individuals may experience dry mouth, which can result from hormonal changes and can increase the risk of tooth decay. Saliva plays a crucial role in protecting teeth from acid and bacteria.
- Gingivitis: Hormonal changes can lead to an increased risk of gum inflammation and gingivitis during pregnancy. This condition can cause redness, swelling, and bleeding of the gums.
While pregnancy can lead to these oral health challenges, it’s important to emphasize that maintaining good oral hygiene practices, including regular brushing, flossing, and dental checkups, can help prevent or mitigate these issues. Additionally, eating a balanced diet that’s rich in nutrients, including calcium and vitamin D, is essential for the health of your teeth and bones.
Dental care during pregnancy is safe and essential for maintaining oral health. If you experience any dental issues or discomfort during pregnancy, it’s advisable to consult with your dentist. They can provide guidance, preventive care, and treatment as needed to ensure that your oral health remains in good condition throughout your pregnancy and beyond.
Which teeth pain during pregnancy?
During pregnancy, tooth pain can occur in any part of the mouth, but certain dental issues are more commonly associated with specific areas of tooth pain. Common dental problems that can lead to tooth pain during pregnancy include:
- Tooth Decay (Cavities): Tooth decay can cause localized tooth pain, often felt as a sharp or throbbing ache. The pain is usually concentrated in the affected tooth or teeth.
- Gingivitis: Gingivitis is a common gum problem during pregnancy due to hormonal changes. It can cause gum pain, redness, swelling, and bleeding. The pain associated with gingivitis is typically in the gum tissue surrounding the teeth.
- Pregnancy Tumors: Some pregnant individuals develop pregnancy tumors on the gums, which are non-cancerous growths. These growths can cause localized discomfort or pain, usually around the affected area.
- Tooth Sensitivity: Hormonal changes and dietary habits during pregnancy can lead to increased tooth sensitivity. Sensitivity is often characterized by pain or discomfort when consuming hot, cold, sweet, or acidic foods and beverages. It can affect multiple teeth or specific areas.
- Tooth Grinding (Bruxism): Stress during pregnancy may lead to teeth grinding or clenching (bruxism), which can result in jaw pain and tooth sensitivity. The pain is often experienced in the jaw and the teeth.
- Sinus Congestion: Sinus congestion, which is common during pregnancy, can sometimes lead to referred pain in the upper teeth, particularly the molars, making it feel like a toothache.
- Dry Mouth: Some pregnant individuals experience dry mouth due to hormonal changes. Dry mouth can lead to an increased risk of tooth decay and discomfort in the teeth and oral tissues.
- Infection or Abscess: A dental infection or abscess can cause severe localized tooth pain. The pain is often throbbing and may be accompanied by swelling, fever, and discomfort when chewing.
It’s important to note that while pregnancy can increase the risk of these dental issues, they can occur at any time. If you experience tooth pain or any dental discomfort during pregnancy, it’s advisable to consult with a dentist for a proper diagnosis and appropriate treatment. Dental care during pregnancy is safe and essential for maintaining good oral health. Ignoring dental pain or issues can lead to more significant problems and discomfort, so seeking professional care is crucial.
What toothpaste is best for pregnancy?
Choosing the right toothpaste during pregnancy is important for maintaining good oral health and minimizing any potential discomfort or issues related to pregnancy. The best toothpaste for pregnancy is one that is fluoride-containing and suits your individual oral health needs. Here are some factors to consider when selecting toothpaste during pregnancy:
- Fluoride: Look for toothpaste that contains fluoride, as fluoride is essential for preventing tooth decay and strengthening tooth enamel. The American Dental Association (ADA) recommends fluoride toothpaste for everyone, including pregnant individuals. The fluoride concentration in toothpaste is generally safe when used as directed.
- ADA Seal of Acceptance: Choose toothpaste with the ADA Seal of Acceptance, which indicates that the product has met the ADA’s criteria for safety and effectiveness.
- Gentle and Mild: Some pregnant individuals may experience increased sensitivity or oral discomfort. If you have sensitive teeth or gums, consider using a toothpaste that is labeled as “gentle” or “for sensitive teeth and gums.”
- Antibacterial Properties: If you are prone to gum problems like gingivitis during pregnancy, you may benefit from a toothpaste that has antibacterial properties, such as those containing triclosan or stannous fluoride. These can help reduce gum inflammation and bacteria.
- Flavor and Texture: Choose a toothpaste with a flavor and texture that you find pleasant, as this can make brushing more enjoyable and encourage good oral hygiene habits.
- Avoid Harsh Ingredients: Check the toothpaste ingredients to make sure it does not contain harsh abrasives or strong additives that may be too abrasive for your teeth or gums.
- Consult Your Dentist: If you have specific dental concerns or conditions, such as tooth sensitivity or gum problems, consult your dentist. They can recommend a toothpaste that addresses your specific needs.
Remember that proper brushing technique and consistency are just as important as the toothpaste you use during pregnancy. Brush your teeth at least twice a day, for two minutes each time, using a soft-bristle toothbrush. Floss daily, and consider using an antimicrobial or fluoride mouthwash, if recommended by your dentist.
Regular dental checkups are crucial during pregnancy to monitor your oral health and address any issues promptly. If you have questions or concerns about choosing the right toothpaste for your pregnancy, consult your dentist or healthcare provider for personalized recommendations based on your oral health needs.